Yew Needle Blight
Contact
Plant Diagnostician
Phone: (479) 575-2727
Email: ssmith@uada.edu
Jason Pavel
Diagnostician
Phone: (479) 575-7257
Email: jpavel@uada.edu
Office:
University of Arkansas System Division of Agriculture
Cralley Warren Building
Room 16
2601 N. Young Ave.
Fayetteville, AR 72704
Yew Needle Blight
Plant Health Clinic Disease Note Issue 27
Sherrie Smith and Jason Pavel
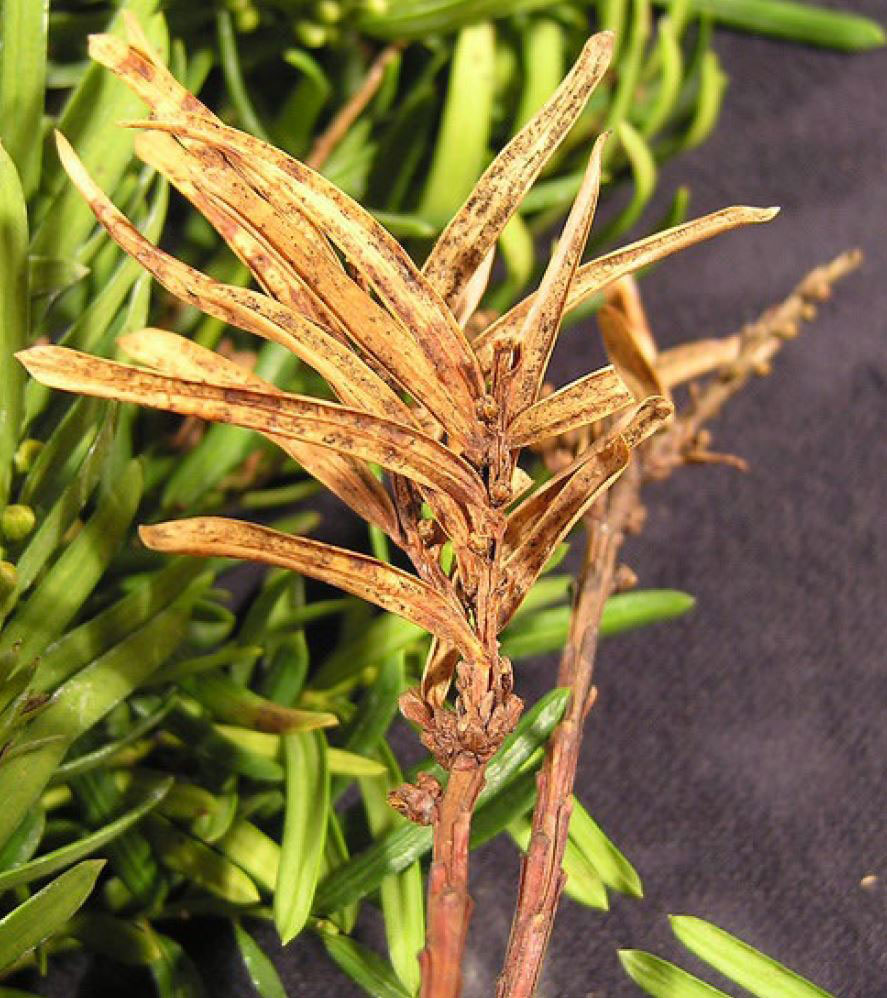

Yews are attractive, soft needled evergreen shrubs that are planted extensively as specimen plants and as hedges in landscapes. Some species grow quite large, but they tolerate pruning very well. Yews tolerate a range of growing conditions if they are on good soil with excellent drainage. In the south yews prefer afternoon shade. When their requirements are met, yews present few problems.
What is Yew Needle Blight?
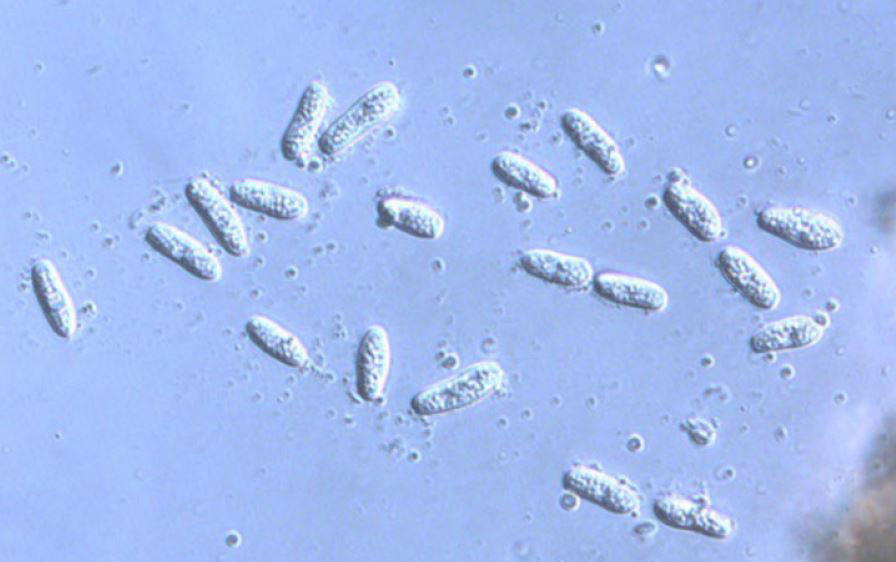
We sometimes will receive a sample of yew with a needle blight caused by the fungus Gloeosporium taxicola. This fungus causes browning of needles, followed by needle cast. When viewed with a magnifying glass, the small pustule-like fruiting bodies of the fungus may be observed.
How do I treat Yew Needle Blight?
Treatment consists of pruning out the damaged twigs and applying fungicides. Fungicides such as Bio Advanced Garden-Disease Control for Roses, Flowers, Shrubs (tebuconazole), or Fertilome Liquid Systemic Fungicide (propiconazole), or Green Light Fung-Away Fungicide (triadmefon), or Fertilome Liquid Fungicide (chlorothalonil) may be used, among others.
Take Aways:
• Avoid overhead irrigation.
• Begin fungicide treatment as first sign of disease.
Follow us on Facebook!
This work is supported by the Crop Protection and Pest Management Program [grant no. 2017-70006- 27279/project accession no. 1013890] from the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.